
2015 Chicago Regional Bridge Building Specifications
These rules have been developed by the Chicago Regional Bridge Building
Committee for the 2015 Chicago Regional Bridge Building Contest
to be held
on Tuesday, January 27, 2015 at Illinois Institute of
Technology, Chicago IL 60616, USA.
Questions about these rules should be directed to Dr. John Kallend, by
email at kallend@iit.edu.
This is a contest for individual high school students, not
teams. The object of this contest is to see who can design, construct and
test the most efficient bridge within these specifications. Model
bridges are intended to be simplified versions of real-world bridges,
which are designed to accept a load in any position and permit the load to
travel across the entire bridge. In order to simplify the model bridge
design process, the number of loading positions has been reduced,
and to allow the contest to proceed in a reasonable amount of time, only
one loading position is actually tested. These simplifications do not
negate the requirement that the bridge must be designed to accept a load
at any of the positions. Bridges determined by the judges to not
meet this requirement will be disqualified and tested as unofficial
bridges.
1. Materials
-
The bridge must be constructed only from 3/32 inch square
cross-section basswood and any commonly available adhesive.
Kits of basswood are available from the the IIT Office of Admissions,
contact Margarita Fraga,
fragam@iit.edu, for information.
-
The basswood may be notched, cut, sanded or laminated in any manner
but must still be identifiable as basswood.
-
No other materials may be used. The bridge may not be stained,
painted or coated in any fashion with any foreign substance.
2. Construction
-
The bridge mass shall be no greater than 30.00 grams.
-
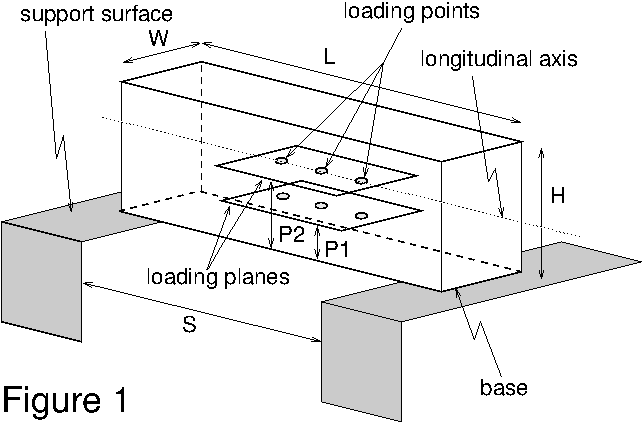
The bridge (see Figure 1) must span a gap (S) of 300. mm,
be no longer (L) than 400. mm, have a maximum width
(W) of 80. mm, be no taller (H) than 200. mm
above the support surfaces.
-
No portion of the bridge may extend below the top of the support
surfaces.
-
The two loading planes (P1 and P2) shall be horizontal
and shall lie between 0. mm and 10. mm (P1) and
50. mm and 60. mm (P2) above the support surfaces.
-
The bridge must be constructed such that both loading planes are
continuous with clearance provided for the loading rod to be attached
to the plate and hang down vertically through the bridge below each
loading point (see section 3 below) . No
optimization for a specific plane or loading position will be
permitted.
3. Loading
-
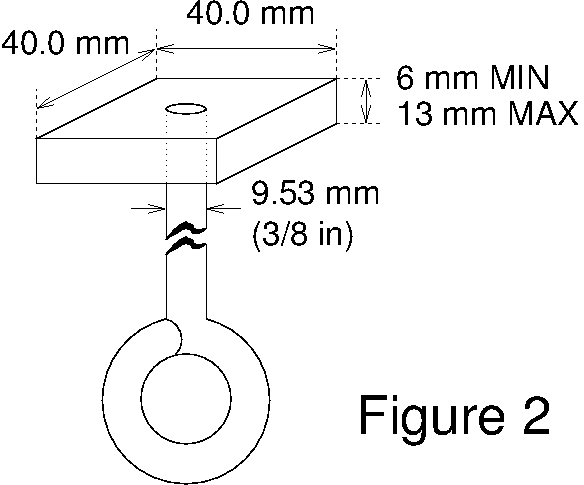
The load will be applied downward, from below, by means of a
40.0 mm square plate (see Figure 2) resting on the loading plane
of the bridge. The plate will be 6.35 mm (1/4 inch) thick and will
have a 9.53 mm (3/8 inch) diameter eyebolt attached from below at
its center. Masses will be supported on a vertical loading rod
suspended from the eyebolt.
-
The two edges of the loading plate will be parallel to the
longitudinal axis of the bridge at the time of load application.
-
The load will be applied on the longitudinal axis of the bridge at one
of six loading points: center and 50. mm on either side of the
center of the 300. mm span on each of the two loading
planes.
4. Testing
-
On the day of the contest, a 6-sided die will be cast to determine
which loading location is to be used. It will be the same for all
bridges.
-
The bridge will be centered on the support surfaces.
-
The loading plate will be placed on the bridge at the specified
loading location and the load will be applied from below, as described
in section 3 above.
-
Competition loading will stop at 50. kg. However, loading will
continue until bridge failure.
-
Bridge failure is defined as the inability of the bridge to carry
additional load, or a load deflection of 25. mm under the
loading location, whichever occurs first.
-
The bridge with the highest structural efficiency, E, will be
declared the winner. Bridges failing above 50. kg will be
considered to have held 50. kg for efficiency calculation.
E = Load supported in grams (50,000g maximum) / Mass of bridge in grams
5. Qualification
-
All construction and material requirements will be checked prior to
testing. Bridges failing to meet these requirements will be
disqualified. If physically possible, disqualified bridges may be
tested as exhibition bridges at the discretion of the builder and the
contest directors.
-
If, during testing, a condition becomes apparent (i.e., use of
ineligible materials, inability to support the loading plate, bridge
optimized for a single loading point, etc.) which is a violation of
the rules or prevents testing as described above in Section 4, that bridge shall be disqualified.
-
Decisions of the judges are final; these rules may be revised as
experience shows the need. Please check our web site,
http://bridgecontest.phys.iit.edu
after January 15, 2015, to learn whether any changes have been made.
Last update: October 10, 2014
[ Bridge Contest Home ] [ International Contest ] [ Chicago Regional Contest ]
[ Region Locator ] [ Official Documentation ] [ Other Bridge Links ]
For further information, contact: Prof. Carlo Segre -
segre@iit.edu,
Illinois Institute of Technology
© International Bridge Building Committee, 2024



